Efecto gastroprotector del extracto de Hypericum perforatum sobre la úlcera gástrica inducida por indometacina en ratas
Gastroprotective effect of Hypericum perforatum extract on indomethacin induced gastric ulcer in rats

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
Mostrar biografía de los autores
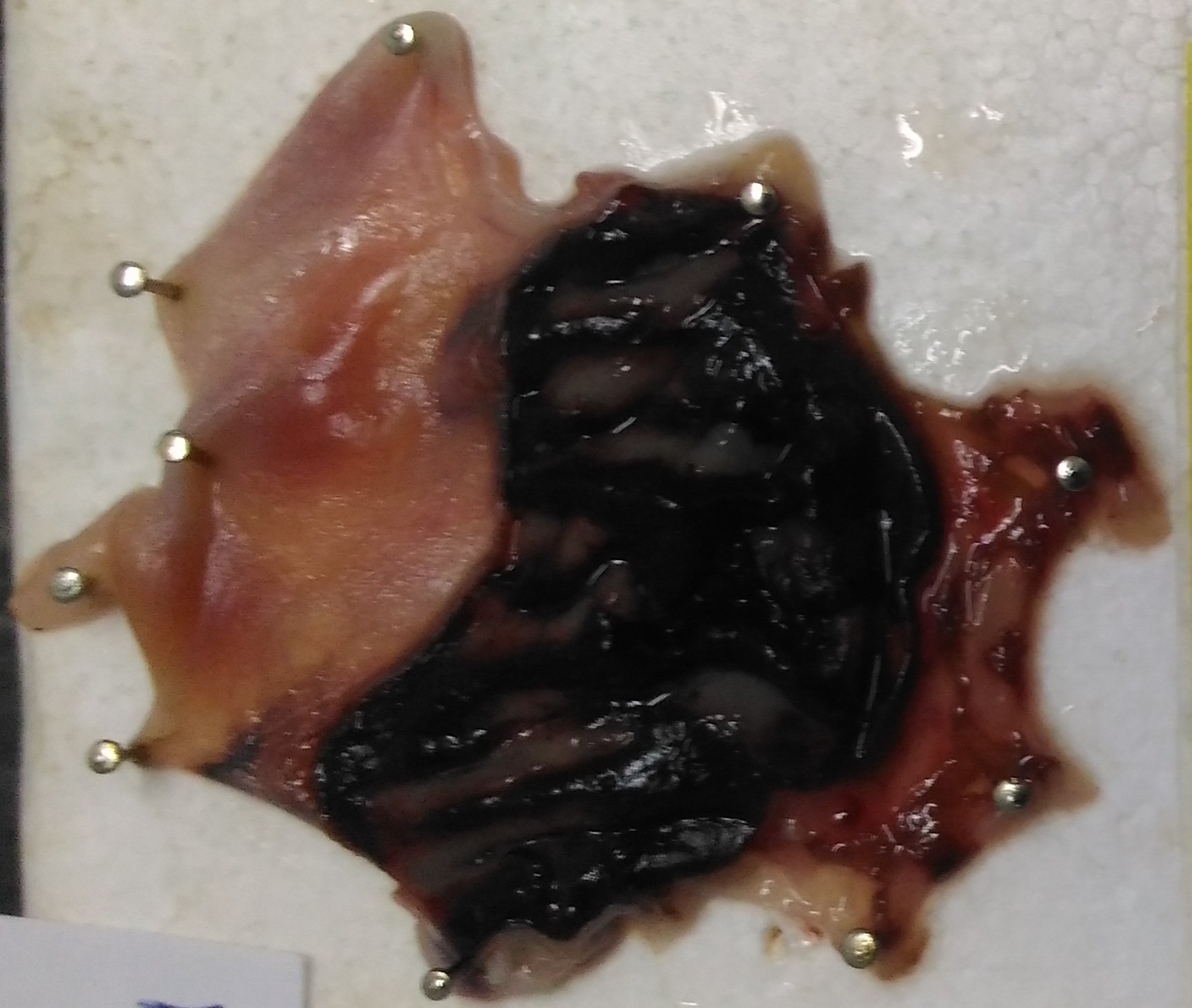
Objetivo. Hypericum perforatum L. (H. perforatum) es una hierba tradicional utilizada en el tratamiento de muchas enfermedades. El extracto de H. perforatum tiene efectos antimicrobianos, antioxidantes, antiinflamatorios, antiulcerosos y antidepresivos. La indometacina es un fármaco antiinflamatorio no esteroideo. Puede causar daño oxidativo en el tejido del estómago. Para este propósito, se investigó la eficacia protectora del extracto de H. perforatum en un modelo de úlcera gástrica inducida por indometacina. Materiales y métodos. Se utilizaron sesenta ratas macho albinas Wistar y las ratas se dividieron en 6 grupos como control negativo, control positivo, H. perforatum, extracto de H. perforatum+indometacina 10/25, extracto de H. perforatum+indometacina 25/25, extracto de H. perforatum+indometacina 50/25. Se administraron por vía oral diferentes dosis de extracto de H. perforatum por sonda, y después de 5 minutos se indujo la úlcera gástrica con indometacina (25 mg/kg). Después de 6 horas, se sacrificaron las ratas. Se midieron los índices de úlceras para cada estómago. Se analizaron los niveles de glutatión (GSH), catalasa (CAT), malondialdehído (MDA) y superóxido dismutasa (SOD) en el tejido del estómago. Resultados. El extracto de H. perforatum+indometacina 50/25 aumentó la actividad de SOD y el nivel de GSH y disminuyó los niveles de MDA en la úlcera gástrica inducida por indometacina. Sin embargo, el índice de úlcera fue significativamente menor solo en el grupo que recibió el extracto de H. perforatum. Conclusiones. Este estudio indica que el extracto de H. perforatum puede tener como potencial agente alternativo en el tratamiento de la úlcera gástrica inducida por indometacina.
Visitas del artículo 708 | Visitas PDF
Descargas
- Guyton AC. Texbook of Medical Physiology. Physiology of Gastrointestinal Disorders. 11thed. Philadelphia: Saunders Company; 2006; 819-822. https://www.moscmm.org/pdf/Guyton%20physiology.pdf
- Kaya S. Veteriner Farmakoloji 5. Baskı Cilt 2, Kaya S, Pirinçci İ, Ünsal A, Traş B, Bilgili A, Akar F (eds) Medisan Yayınevi: Ankara; 2009.
- Kurumbail R, Kiefer JR, Marnett LJ. Cyclooxygenase enzymes: Catalysis and inhibition. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001; 11(6):752-760. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-440x(01)00277-9
- Suleyman H, Demircan B, Karagoz Y. Anti-inflammatory and side effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rep. 2007; 59:247-258. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17652824/
- Baskose I, Savran A. A new species from southern Anatolia (Dedegöl Mountain Series — Çürük Mountain) in Turkey: Hypericum bilgehan-bilgilii (Hypericaceae). Phytotaxa. 2018; 374(2):110-118. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.374.2.2
- Ersoy E, Özkan EE, Mat A. Pharmacological Actiivities of Hypericum Species in Light of New Studies. JARHS. 2019; 2(2):71-79. https://doi.org/10.26650/JARHS2019-616370
- Greeson J, Sanford B, Monti DA. St. John’s worth (Hypericum perforatum): a review of the current pharmacological, toxicological and clinical literature. Psychopharmacology 2001; 153:402-414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000625
- Öztürk N, Korkmaz S, Öztürk Y. Wound-healing activity of St. John’s Wort (L.) on chicken embryonic fibroblasts. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007; 111:33-39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2006.10.029
- Prisacaru AI, Andritoiu C, Andriescu C. Evaluation of the wound-healing effect of a novel Hypericum perforatum ointment in skin injury. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2013; 54(4):1053-1059. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24399001/
- Kıyan S, Uyanıkgil Y, Altuncı YA, Çavuşoğlu T, Uyanikgil EOC, Karabey F. Investigation of acute effects of Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort-Kantaron) treatment in experimental thermal burns and comparison with silver sulfadiazine treatment, Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2015; 21: 323-336. https://dx.doi.org/10.5505/tjtes.2015.63822
- Arsić I, Žugić A, Antić DR, Zdunić G, Dekanski D, Marković G, Tadić V. Hypericum Perforatum L. Hypericaceae/Guttiferae Sunflower, Olive and Palm Oil Еxtracts Attenuate Cold Restraint Stress –Induced Gastric Lesions. Molecules 2010; 15:6688-6698. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15106688
- Karaboğa İ, Dökmeci AH, Ovalı MA, Yılmaz A. Etanol Uyarımlı Sıçan Akut Mide Mukoza Hasar Modelinde Hypericum perforatum’un Koruyucu Etkilerinin İncelenmesi. NKMJ 2017; 5(3):99-108. https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/issue-full-file/33411
- Abdel-Salam OME. Anti-Inflammatory, Antinociceptive and Gastric Effects of Hypericum perforatum in Rats. ScientificWorldJournal. 2005; 5:585–596. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2005.78
- Odabaşoğlu F, Halici Z, Cakir A, Halici M, Aygun H. Beneficial effects of vegetable oils (corn, olive and sunflower oils) and α-tocopherol on anti-inflammatory and gastrointestinal profiles of indomethacin rats. Eur. J. Pharmaco. 2008; 591:300-306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.06.075
- Guidobono F, Pagani F, Ticozzi C, Sibilia V, Pecile A, Netti C. Protection by amylin of gastric erosions induced by indomethacin or ethanol in rats. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1997; 120(4): 581-6. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0700941
- Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y. A simple for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem. 1988; 34:497-500. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3349599/
- Aebi H. Catalase in vitro assay methods. Methods in Enzymology. 1984; 105:121-126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05016-3
- Tietze F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal Biochem. 1969; 27(3):502-522. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(69)90064-5
- Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979; 95:351-358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
- Nguelefack TB, Feumebo CB, Ateufack G, Watcho P, Tatsimo S, Atsamo D, Tane P, Kaman-yi A. Anti-ulcerogenic properties of the aqueous and methanol extracts from the leaves of Solanum torvum Swartz (Solanaceae) in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2005; 119(1): 135-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2008.06.008
- Schubert ML. Gastric secretion. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2014; 30: 578-582. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0000000000000125
- Kılıçarslan H, Kalyon S, Yenice N. Etiopathogenesis of Peptic Ulser, Okmeydanı Tıp Dergisi. 2011; 27(2):65-69. http://doi.org/10.5222/otd.2011.065
- Eminler AT, Uslan Mİ, Köksal AŞ, Parlak E. Non-Steroid Anti-İnflamatuvar İlaçların Üst Gastrointestinal Sistem Yan Etkileri ve Önlenmesi. Güncel Gastroenteroloji. 2014; 18(3):333-338. http://guncel.tgv.org.tr/journal/53/pdf/100245.pdf
- Dündar Y, Aslan R. Hekimlikte Oksidatif Stres, Afyon Kocatepe Üniversitesi Yayınları: Ankara; 2000.
- Zdunic G, Godevac D, Milenkovic M, Vucievic D, Savikin K, Menkovic N, et al. Evalution of Hypericum perforatum oil extract for an antiinflammatory and gastroprotective activity in rats. Phytotherapy Research. 2009; 23(11):1559-1564. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.2809
- Kurt H, Özbayer, C, Değirmenci İ, Burukoğlu D, Saadat SM, Üstüner MC, et al. İndomethazine Bağlı Oluşan Gastrik Mukozal Hasar Üzerine Hypericum Perforatum Yağının Koruyucu Etkisi. Bozok Tıp Derg. 2016; 6(3):46-52. https://app.trdizin.gov.tr/makale/TWpVM05qQTFOUT09/indomethazine-bagli-olusan-gastrik-mukozal-hasar-uzerine-hypericum
- Cayci MK, Dayioglu H. Hypericum perforatum extracts healed gastric lesions induced by hypothermic restraint stress in Wistar rats. Saudi Med J. 2009; 30(6):750-754. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19526154/
- Vieira SM, Silva RL, Lemos HP, Amorim RC, Silva EC, Reinach PS, Cunha FQ, Pohlit AM, Cunha TM. Gastro-protective effects of isobrucein B, a quassinoid isolated from Picrolemma sprucei. Fitoterapia. 2014; 95:8-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2014.02.008
- Diniz PB, Ribeiro AR, Estevam CS, Bani CC, Thomazzi SM. Possible mechanisms of action of Caesalpinia pyramidalis against ethanol-induced gastric damage. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015; 20(168):79-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.054
- Yoshiwaka T, Naito Y, Kishi A, Tomii T, Kaneko T, Iinuma S, et al. Role of active oxygen, lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in the pathogenesis of gastric mucosal injury induced by indomethacin in rats. Gut. 1993; 34(6):732-737. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.34.6.732
- Dengiz GÖ, Gürsan N. Effects of Momordica charantia L. (Cucurbitaceae) on indomethacin-induced ulcer models in rats. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2005; 16(2):85-88. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16252198/
- Kim JH, Kim BW, Kwon HJ, Nam SW. Curative Effect of Selenium Against Indomethacin- Induced Gastric Ulcers in Rats. Microbial Biotechnology. 2011; 21(4):400-404. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21532324/
- El-Masry TA, Elahwel AM, Emara AM. Study on treating ethanol-induced gastric lesions with omeprazole, Nigella sativa oil or both. Toxicological and Enviromental Chemistry. 2010; 92:1765-1782. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772241003730589
- Boyacioglu M, Kum C, Sekkin S, Yalinkilinc HS, Avci H, Epikmen ET, Karademir U. The effects of lycopene on DNA damage and oxidative stress on indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Clin Nutr. 2016; 35:428-435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2015.03.006
- Chattopadhyay I, Bandyopadhyay U, Biswas K, Maity P, Banerjee RK. Indomethacin inactivates gastric peroxidase to induce reactive-oxygen-mediated gastric mucosal injury and curcumin protects it by preventing peroxidase inactivation and scavenging reactive oxygen. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006; 40:1397-1408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.12.016























